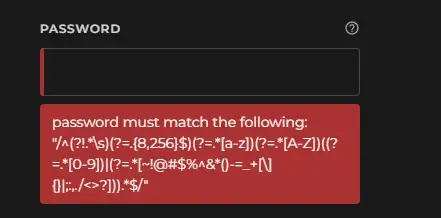
Those (?=...) bits are positive lookahead assertions:
Lookaround assertions are zero-width patterns which match a specific pattern without including it in $&. Positive assertions match when their subpattern matches, negative assertions match when their subpattern fails. Lookbehind matches text up to the current match position, lookahead matches text following the current match position.
The one (?!...) is a negative lookahead assertion.
The $& var doesn't really matter outside of Perl. It contains the text of the pattern you just matched, but even within Perl, capture groups are preferred. Once used at all, it will slow down your program every time a new regex is hit, which is especially bad in long running web server environments. Gets used sometimes in short scripts, though.
What really matters is that the lookaheads don't consume any text. In other words, the pointer that shows where in the text we are doesn't increment; once we're outside of the lookahead, we're still right back in the same place.
So let's break this down using the /x modifier to make it somewhat sane.
/^
(?!.*\s) # no whitespace allowed
(?=.{8,256}$) # between 8 and 256 characters (the '$' here indicating the end of the string)
(?=.*[a-z]) # has to be a lowercase ASCII alphabet char somewhere
(?=.*[A-Z]) # has to be an uppercase ASCII alphabet char somewhere
( # need a number, or a list of special chars on a US keyboard
(?=.*[0-9])
| (?=.*[~!@#$%^&*()-=_+[\]{}|;:,./<>?])
)
.* # consumes the whole string
$/x
Notes:
- Doesn't make any allowances for non-English characters, or even non-US characters (like the "£" character in the UK)
- There's a whole slew of utf8 characters out there that should count towards "special characters", but aren't considered here
- There's no reason to deny whitespace; let people use passphrases if they want (but then, you also don't want to block those people for not using symbols)
- Putting a limit at 256 is questionable, but may not necessarily be wrong
That last one has some nuance. We often say you shouldn't put any upper limit, but that's generally not true in the real world. You don't want someone flooding an indefinite amount of data into any field, password or not. A large limit like this is defensible.
Also, lots of devs are surprised to learn that bcrypt and scrypt have a length limit of 72 bytes. A way around this is to run your input through SHA256 before giving it to bcrypt or scrypt.