39
NASA May Pay $1 Billion to Destroy the International Space Station. Here's Why
(www.scientificamerican.com)
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
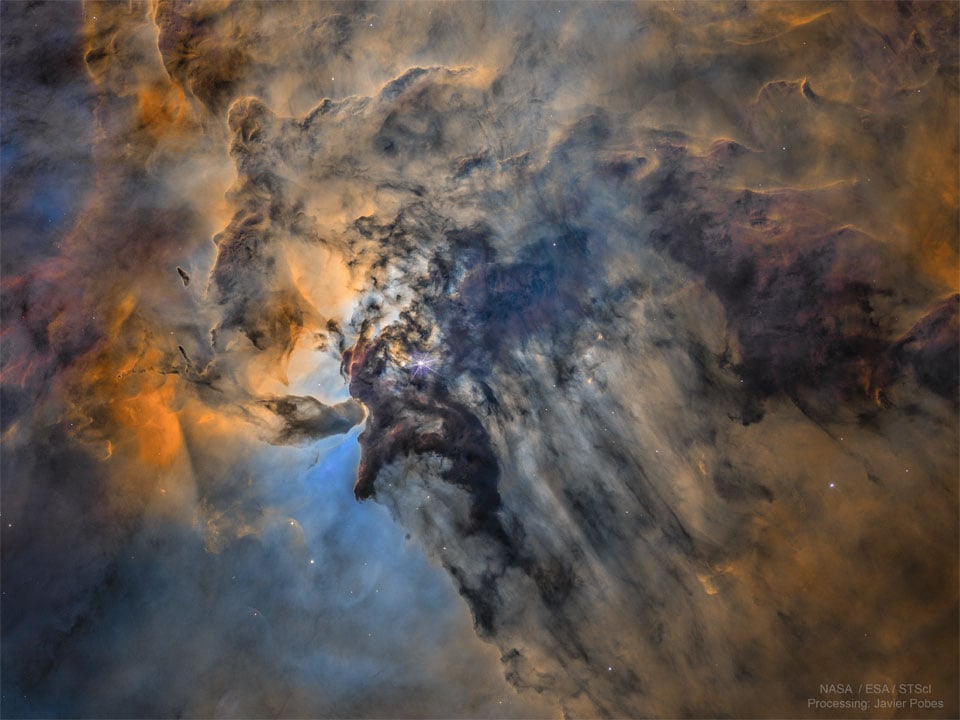 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
🔭 Science
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
It would require more energy than just deorbiting it. So, yes, it's possible, but even more expensive.