The War Room
Community for various OSINT news and subject matter for open discussion or dissemination elsewhere
Check Point to Acquire SASE Security Firm Perimeter 81 for $490 Million
Check Point will acquire SASE and ZTNA cybersecurity firm Perimeter 81 for $490 million, a big discount to its $1 billion valuation in 2022.
The post Check Point to Acquire SASE Security Firm Perimeter 81 for $490 Million appeared first on SecurityWeek.
EvilProxy Cyberattack Flood Targets Execs via Microsoft 365
A campaign sent 120,000 phishing emails in three months, circumventing MFA to compromise cloud accounts of high-level executives at global organizations
The Hard Realities of Setting AI Risk Policy
Time to get real about what it takes to set and enforce cybersecurity and resilience standards for AI risk management in the enterprise.
Microsoft Exchange updates pulled after breaking non-English installs

Microsoft has pulled Microsoft Exchange Server's August security updates from Windows Update after finding they break Exchange on non-English installs.
On August 8th, Microsoft released new Exchange Server security updates during the August 2023 Patch Tuesday.
These security updates fix six vulnerabilities, including four remote code execution flaws, one elevation of privileges flaw, and a spoofing vulnerability that can be used to conduct an NTLM Relay Attack.
However, after Microsoft Exchange admins began installing the new updates on non-English servers, they found that the Exchange Windows services were no longer starting.
"Apparently the update cannot be successfully installed on operating systems and Exchange servers in German," warned IT architect Frank Zoechling.
"The setup fails with the error code 1603 and leaves a faulty Exchange installation. Users of Exchange servers and operating systems in German should therefore not install the update for the time being."
Microsoft has since updated the August 2023 Exchange Server Security Updates bulletin, warning admins that they temporarily removed the update from Windows and Microsoft Update while they investigate the issue.
"We are aware of Setup issues on non-English servers and have temporarily removed August SU from Windows / Microsoft update," explains Microsoft.
"If you are using a non-English language server, we recommend you wait with deployment of August SU until we provide more information."
A dedicated support article sheds more light on the issue, stating that the problems are caused by a "localization issue in the Exchange Server August 2023 SU installer".
Microsoft says that when you install the Microsoft Exchange Server 2019 or 2016 security updates on non-English operating systems, the installer will stop and roll back changes, leaving the Exchange Server Windows services in a disabled state.
For those impacted by the problematic install, Microsoft has shared the following steps that can be used to enable the Windows servers and start Exchange Server:
- If you’ve already tried to install the SU, reset the service state before you run Setup again. You can do this by running the following PowerShell script in an elevated PowerShell window:
- Change to the following directory: \Exchange Server\V15\Bin.
- Enter .\ServiceControl.ps1 AfterPatch, and then press Enter.
- Restart the computer.
- In Active Directory (AD), create an account that has the specific name that’s provided in this step. To do this, run the following command:
New-ADUser -Name "Network Service" -SurName "Network" -GivenName "Service" -DisplayName "Network Service" -Description "Dummy user to work around the Exchange August SU issue" -UserPrincipalName "Network Service@$((Get-ADForest).RootDomain)" 3. Wait for AD replication (up to 15 minutes), and then restart the Exchange Server SU installation. Setup should now run successfully. 4. After the installation finishes, run the following commands:
$acl = Get-Acl -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSIPC\Server"
$rule = New-Object System.Security.AccessControl.RegistryAccessRule((New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier("S-1-5-20")), 983103, 3, 0, 0)
$acl.SetAccessRule($rule)
Set-Acl -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MSIPC\Server" -AclObject $acl
5. Restart the Exchange server to complete the installation.
6. After all Exchange servers are updated, you can safely delete the AD account that was created in step 2.
Once you complete these steps and restart the Exchange server, the Windows services should properly start again and Exchange will be back up and running.
For users running English localizations of Windows, it is still advised to download and install the updates to be protected from the disclosed vulnerabilities.
Reflecting on supply chain attacks halfway through 2023
With BlackHat and “Hacker Summer Camp” going on over the next few weeks, this seems like the right time to step back and reflect on what’s happened so far this year.
CISA discovered a new backdoor, named Whirlpool, used in Barracuda ESG attacks
The U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) observed a new backdoor, named Whirlpool, in attacks on Barracuda ESG appliances. The U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has discovered a new backdoor, named Whirlpool, that was employed in attacks targeting Barracuda ESG devices. At the end of May, the network security solutions provider Barracuda warned […]
The post CISA discovered a new backdoor, named Whirlpool, used in Barracuda ESG attacks appeared first on Security Affairs.
MoustachedBouncer hackers use AiTM attacks to spy on diplomats

Image: Midjourney
A cyberespionage group named 'MoustachedBouncer' has been observed using adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks at ISPs to hack foreign embassies in Belarus.
According to an ESET report released today, the researchers observed five distinct campaigns, with the threat actors believed to be active since at least 2014, using AitM at Belarusian ISPs since 2020.
The two signature malware frameworks MoustachedBouncer used during this time are 'NightClub,' since 2014, and 'Disco,' introduced in 2020 to support data theft, capturing screenshots, recording audio, and more.
.jpg)
MoustachedBouncer campaigns
Source: ESET
AiTM attacks
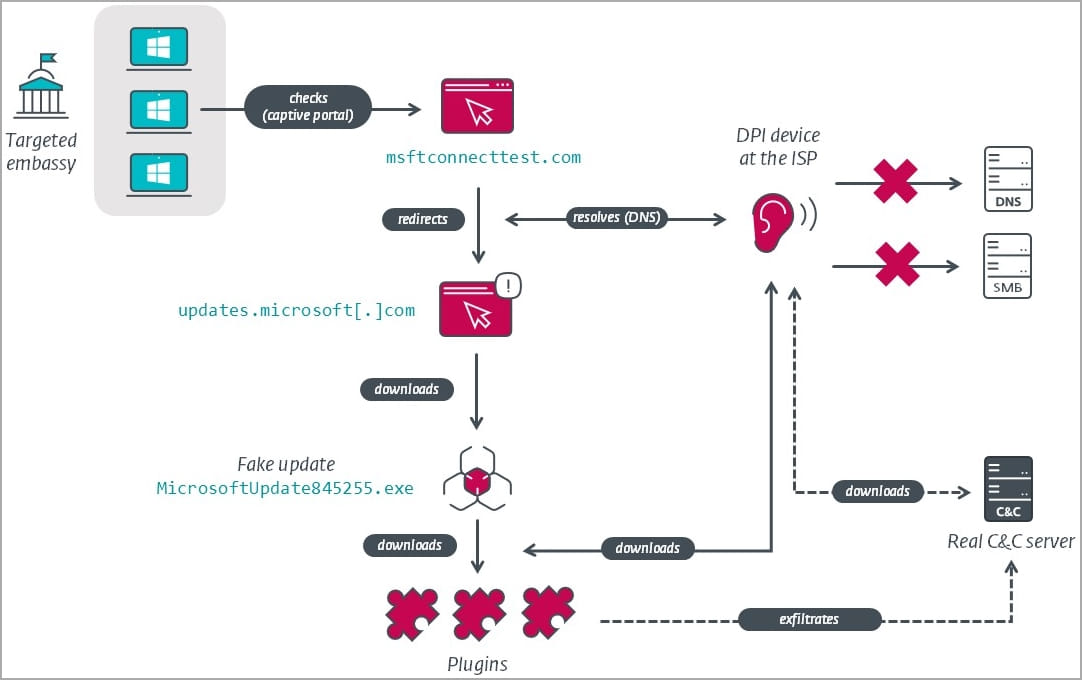
The recent method used to breach networks is to use adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks at the ISP level to trick targeted Windows 10 installation into assuming it stands behind a captive portal.
The ISPs confirmed to be used by MoustachedBouncer are Beltelecom (wholly state-owned) and Unitary Enterprise AI (largest private).
ESET believes the threat actors achieve this by manipulating the traffic either by breaching the ISP infrastructure or collaborating with entities that have access to the network service providers in Belarus.
"For IP ranges targeted by MoustachedBouncer, the network traffic is tampered at the ISP level, and the latter URL redirects to a seemingly legitimate, but fake, Windows Update URL, "updates.microsoft[.]com," explains ESET's report.
"Hence, the fake Windows Update page will be displayed to a potential victim upon network connection."
When a targeted Windows 10 device connects to the network, it will redirect captive portal checks (used to check if a device is connected to the internet) to a Fake Windows update HTML page.
This page uses JavaScript to display a "Get Updates" button that, when clicked, causes a fake operating system update ZIP file to be downloaded.
This ZIP file contains a Go-based malware that creates a scheduled task that executes every minute, fetching another executable, the malware loader, from what appears like a Google Cloud IP address but is likely just there for cover.
The malware payloads the MoustachedBouncer has used since 2014 are various versions of the 'NightClub' and 'Disco' malware toolkits, showcasing notable evolution with each new release.
Observed infection chain
Source: ESET
NightClub malware
NightClub was the first malware framework used by the espionage group, with distinct samples retrieved by ESET's analysts in 2014, 2017, 2020, and 2022.
Early versions featured file monitoring and SMTP (email) exfiltration and command and control server communications, while its authors later added a persistence mechanism and a keylogger,
The latest version of NightClub, used by the hackers between 2020 and 2022, features new modules for taking screenshots, recording audio, keylogging, and setting up a DNS-tunneling backdoor for C2 communications.
The DNS backdoor implements additional commands that give the malware file, directory creation, reading, and searching functions, and process manipulation capabilities.
Also, the newest NightClub uses a hardcoded private RSA-2048 key for encrypting its strings, while its configuration is stored in an external file, giving it more stealth and versatility.
ESET couldn't determine the infection channel that MoustachedBouncer used for NightClub, so that aspect remains unknown.
Disco malware
Disco is a newer malware framework reaching victims through the previously described AitM-based attack chain, which MoustachedBouncer started using in 2020.
Disco uses multiple Go-based plugins that expand its functionality, allowing the malware to:
- Take screenshots every 15 seconds (three modules)
- Execute PowerShell scripts (two modules)
- Exploit CVE-2021-1732 using a publicly-available PoC to elevate privileges
- Set up a reverse proxy using code inspired by the open-source tool 'revsocks' (two modules)
Disco also uses SMB (Server Message Block) shares for data exfiltration, a protocol primarily used for shared access to files, printers, and serial ports, so there's no direct transfer to the C2 server.
MoustachedBouncer's C2 infrastructure is not accessible directly from the public internet, effectively hiding it from security researchers and protecting it from takedowns.
ESET recommends that diplomats and embassy employees based in Belarus use end-to-end encrypted VPN tunnels when accessing the internet to block the AiTM attacks.
Cybersecurity: It's Time to Trust the Machines
When it comes to cybersecurity automation, the pluses outweigh the minuses.
CISA: New Whirlpool backdoor used in Barracuda ESG hacks

Image: Midjourney
The U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has discovered a new backdoor malware named 'Whirlpool' used in attacks on compromised Barracuda Email Security Gateway (ESG) devices.
In May, Barracuda revealed a suspected pro-China hacker group (UNC4841) had breached ESG (Email Security Gateway) appliances in data-theft attacks using the CVE-2023-2868 zero-day vulnerability.
CVE-2023-2868 is a critical severity (CVSS v3: 9.8) remote command injection vulnerability impacting Barracuda ESG versions 5.1.3.001 through 9.2.0.006.
It was later discovered that the attacks started in October 2022 and were used to install previously unknown malware named Saltwater and SeaSpy and a malicious tool called SeaSide to establish reverse shells for easy remote access.
Instead of fixing devices with software updates, Barracuda offered replacement devices to all affected customers at no charge, indicating that the attacks were more damaging than originally thought.
CISA has since shared further details about an additional malware named Submariner that was deployed in the attacks.
New Whirlpool malware
Yesterday, CISA disclosed the discovery of another backdoor malware named 'Whirlpool' [VirusTotal] that was found to be used in the attacks on Barracuda ESG devices.
The discovery of Whirlpool makes this the third distinct backdoor used in the attacks targeting Barracuda ESG, once again illustrating why the company chose to replace devices rather than fix them with software.
"This artifact is a 32-bit ELF file that has been identified as a malware variant named "WHIRLPOOL," reads CISA's updated Barracuda ESG malware report.
"The malware takes two arguments (C2 IP and port number) from a module to establish a Transport Layer Security (TLS) reverse shell."
"The module that passes the arguments was not available for analysis."
From submissions to VirusTotal, the Whirlpool malware appears to have run under the 'pd' process.
Previously, on May 30, 2023, Barracuda found SeaSpy on hacked ESG appliances, a persistent passive backdoor that masquerades as a legitimate service, namely "BarracudaMailService," and runs commands on behalf of the threat actors.
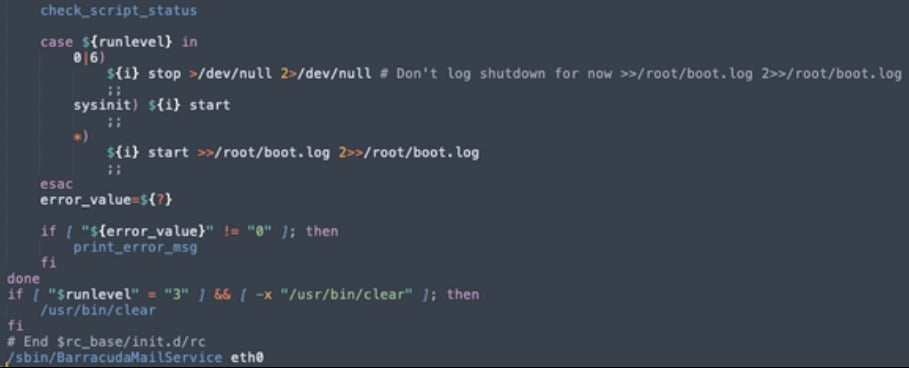
SeaSpy initialization script (CISA)
On July 28, 2023, CISA warned of a previously unknown backdoor in breached Barracuda devices named 'Submarine.'
Submarine resides in the SQL database of ESG, allowing root access, persistence, and command and control communications.
Indicators of compromise and YARA rules that help detect infections by the four newly discovered variants of SeaSpy and Whirlpool are provided in a separate document.
If you identify suspicious activity on your Barracuda ESG appliance or discover signs of compromise by any of the three mentioned backdoors, you are urged to contact CISA's 24/7 Operations Center at "[email protected]" to help with their investigations.
Flashpoint a Strong Performer in External Threat Intelligence Forrester Wave
Forrester has named Flashpoint a Strong Performer in The Forrester Wave™: External Threat Intelligence Service Providers, Q3 2023.
The post Flashpoint a Strong Performer in External Threat Intelligence Forrester Wave appeared first on Flashpoint.
Dell Compellent hardcoded key exposes VMware vCenter admin creds

An unfixed hardcoded encryption key flaw in Dell's Compellent Integration Tools for VMware (CITV) allows attackers to decrypt stored vCenter admin credentials and retrieve the cleartext password.
The flaw is caused by a static AES encryption key, shared across all installs, that is used to encrypt the vCenter credentials stored in the program's configuration file.
Dell Compellent is a line of enterprise storage systems offering features such as data progression, live volume, thin provisioning, data snapshots and cloning, and integrated management.
The software supports storage integration with VMware vCenter, a widely used platform for managing ESXi virtual machines.
However, to integrate the client, it must be configured with VMware vCenter credentials, which are stored in the Dell program's encrypted configuration file.
A hardcoded AES encryption key
LGM Security's researcher Tom Pohl, discovered in a penetration exercise that Dell CITV contains a static AES encryption key that is identical for all Dell customers across all installs.
This AES encryption key is used to encrypt the CITV configuration file containing the program's settings, including the entered vCenter admin credentials.
As AES is a symmetric cipher, it uses the same key for encrypting and decrypting data. This allows an attacker who extracts the key to easily decrypt the configuration file and retrieve the encrypted password.
"The Dell software needs administrative vCenter credentials to function correctly, and it protects those credentials in their config files with a static AES key," Pohl told BleepingComputer.
"Dell is interacting with vCenter servers, and is keeping its credentials in an encrypted confih file that should be completely inaccessible for viewing by anything or anyone other than the Dell software."
"Attackers should not be able to get access to the contents of that file, but it is accessible. However, due to this newly discovered vulnerability, attackers can extract the encryption key that the Dell software is using to protect the contents of that file."
LGM Security's team found that the Dell Compellent software directory contains a JAR file that, when decompiled, revealed a hardcoded static AES key.
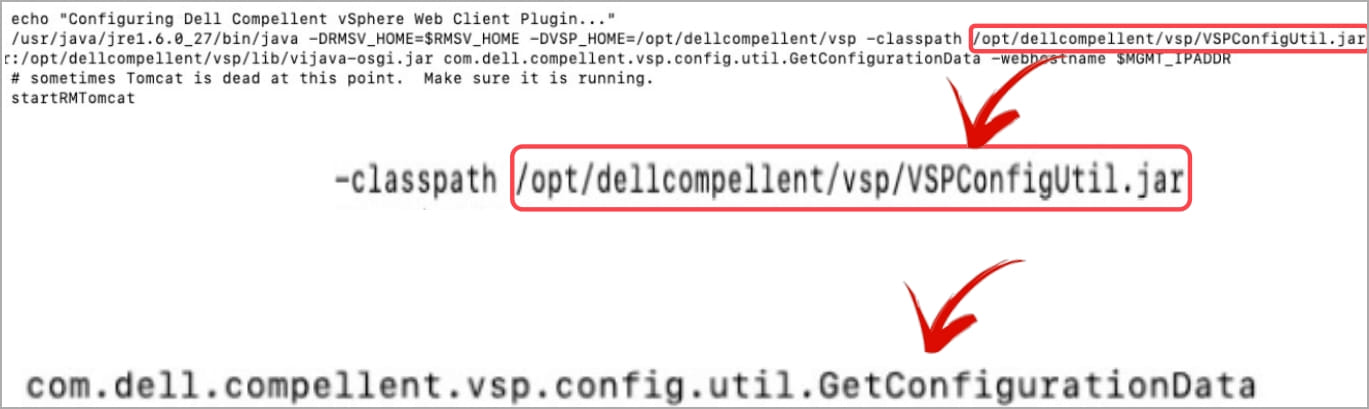
JAR file in a Dell Compellent directory (LGM Security)
Using this AES key, Pohl could decrypt the Dell Compellent configuration file and retrieve the user name and password for the VMware vCenter administrator, as shown below.
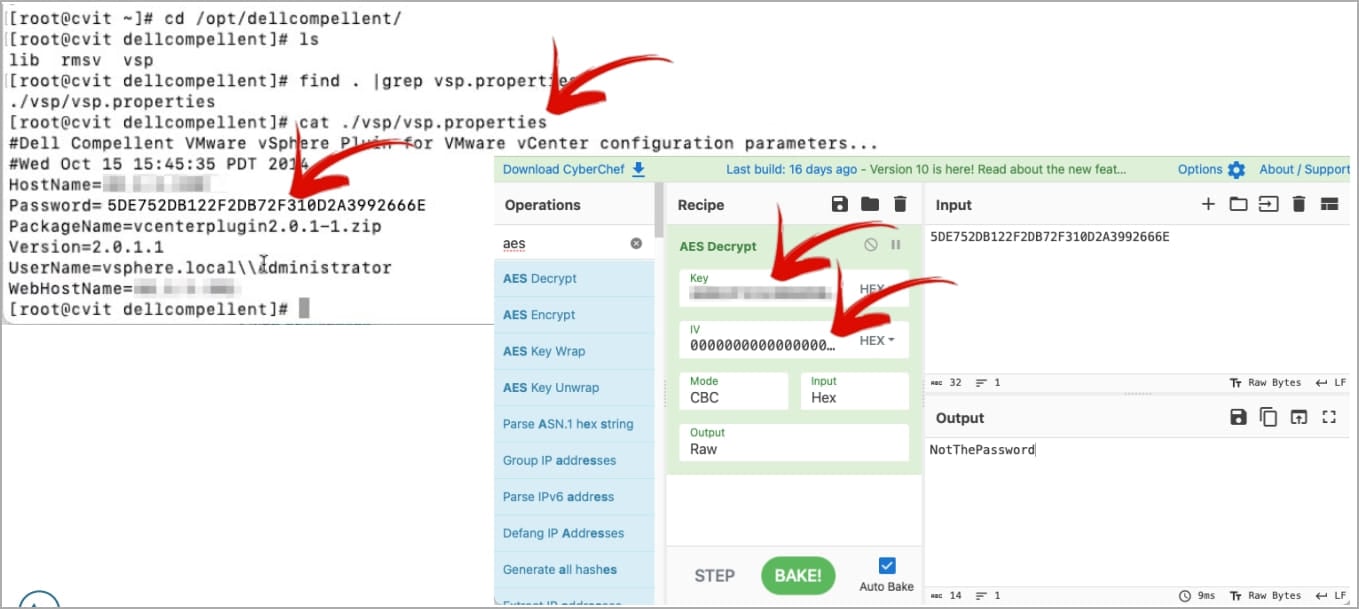
Decrypting admin credentials using the recovered AES key (LGM Security)
The server containing that key was accessible using weak credentials (admin/admin). However, as seen repeatedly, threat actors can gain access to servers in various ways due to vulnerabilities or bad practices.
Also, the issue could be exploitable by rogue insiders or low-privileged external attackers who have access to Dell CITV.
In this instance, the LGM team could have gone further by leveraging access to domain controls but instead opted to create a domain admin account, exploiting the opportunity when a network admin mistakenly left their console unlocked.
Accessing the exposed vCenter server (LGM Security)
The analysts emailed Dell to inform them about their discovery on April 11th, 2023, but the computer and software vendor initially dismissed the report, misunderstanding the scope.
After further communication, Dell promised to roll out a fix by November 2023.
As the standard 90-day vulnerability disclosure policy has expired, Pohl has publicly shared his research in a DEFCON session titled "Private Keys in Public Places."
Pohl discovered similar hardcoded keys in Netgear and Fortinet in 2020, which were subsequently fixed.
Safeguarding Against Silent Cyber Threats: Exploring the Stealer Log Lifecycle

The first seven months of 2023 have seen a continued rapid evolution of the cybercrime ecosystem. Ransomware data exfiltration attacks, stealer log distribution, and new exploits targeting organizations continue to substantially increase.
This article explores a key component of the cybercrime ecosystem, stealer logs, and their role in the broader cybercrime ecosystem.
What are Stealer Logs?
Infostealer malware has risen to prominence as one of the most significant vectors of cybercrime over the past three years.
Infostealers are a form of remote access trojan (RAT) that infects a victim computer, exfiltrates all of the credentials saved in the browser, as well as session cookies, while also stealing other sensitive data such as credit card information, cryptocurrency wallet data, and other information from the host.
Logs are then either used or distributed to other cybercriminals as a key initial vector that enables financial fraud, account takeover attacks, ransomware distribution, and data breaches against organizations.
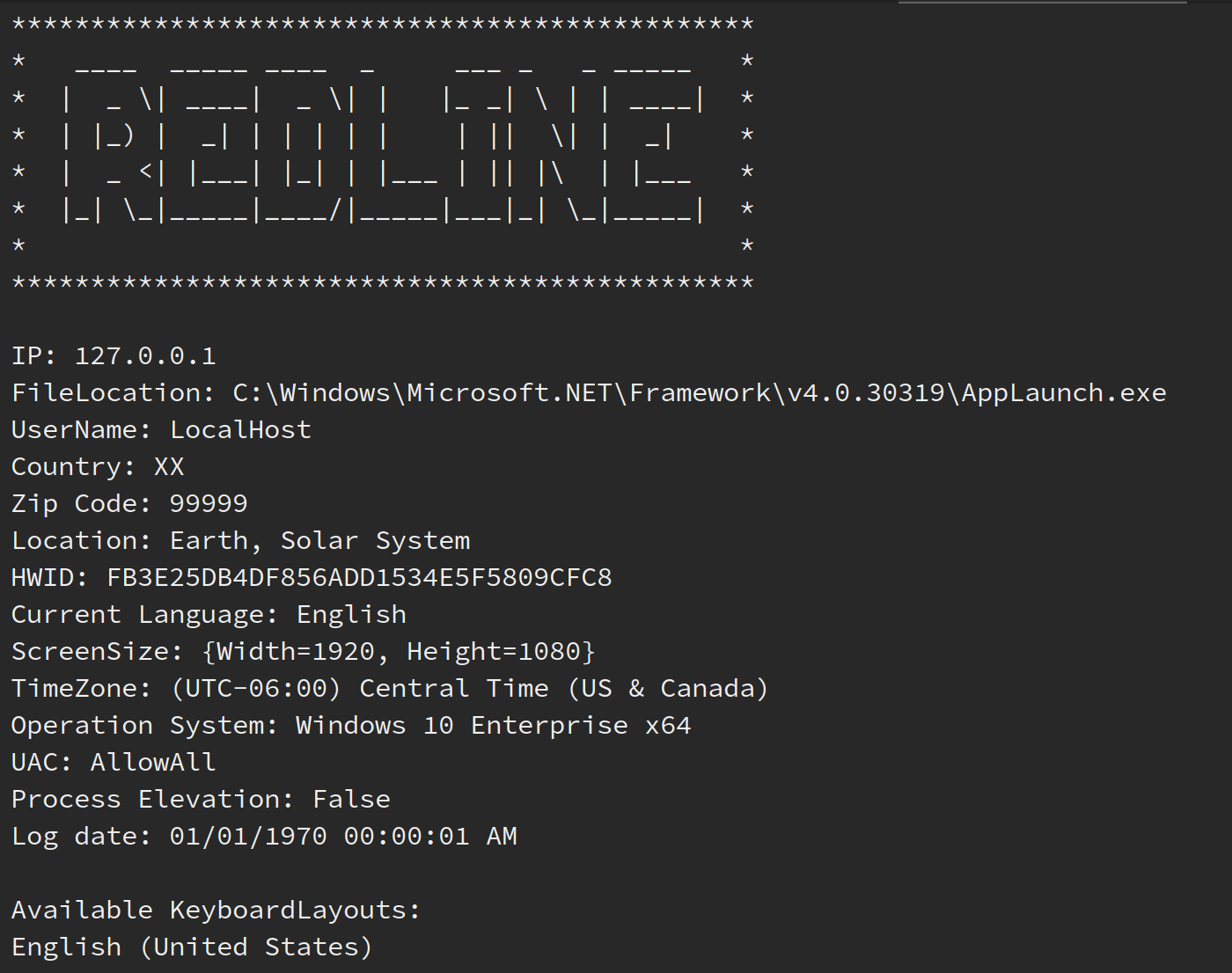
RedLine Stealer log file
Malware as a Service Vendors, Telegram, and the Cybercrime Supply Chain
Malware as a service (MaaS) vendors continually develop new variants of infostealer malware which are then sold in specialized Telegram channels. The most common variants we see today are RedLine, Vidar, and Raccoon.

Description of stealer web panel features
MaaS vendors often package their malware in convenient monthly subscription packages that can be easily purchased for a set amount of cryptocurrency, and come complete with command and control (C2) infrastructure and a backend that enables seamless management of hundreds of thousands of stealer logs.
Threat actors then simply need to identify methods to distribute the malware to consumers.
Distribution typically takes a few forms, some of the most common of which are adding infostealer payloads to cracked software, phishing emails, malvertising, and advertising free video-game currency; infostealer malware is mostly distributed in a “spray and pray” fashion, very rarely being employed in targeted attacks.
Backend for RedLine stealer malware
Once an infection takes place, data is exfiltrated to the malware’s backend infrastructure, in the form of “stealer logs”.
The screenshot on the left shows infrastructure related to a common infostealer variant. The columns display the infection date, country code, checkboxes to mark duplicates, counts of credentials, and finally an automatic parsing system to identify high-value credentials within the log.
Stealer Logs Distribution: Tor and Telegram Take Center Stage
Stealer logs used to be distributed almost exclusively on dark web online stores, through popular autoshops such as Genesis Market and Russian Market.
However, in recent years, there has been an increasing adoption of the messaging platform Telegram for everything related to cyber-crime, including stealer logs distribution; out of more than one million unique logs collected per month, we currently see more than 70% being distributed on Telegram channels.
Stealer logs shared in Telegram channel
Threat actor groups create channels, usually referred to as “clouds”, where they will sell access to freshly gathered stealer logs, for a subscription fee.
On top of selling access to their “private” channels, these groups will usually have a “public” channel, where they distribute what can be considered samples of what a potential buyer would get access to by purchasing a subscription to their “private” channels.
Every day, thousands of stealer logs are distributed across Telegram, spread across hundreds of channels.
Whilst most members of these channels are looking for an easy way to make a quick buck, such as by leveraging stolen cryptocurrency wallets, or access to bank accounts, other more advanced users will look at leveraging the illegitimate access stealer logs provide in order to disrupt corporate operations.
Stealer Logs, Access Brokers and Ransomware Affiliates
We have seen substantial evidence that initial access brokers (IAB), threat actors that operate on dark web forums and sell access to company networks and IT Infrastructure, use logs as a primary vector of initial access.
An initial access broker on the Exploit dark web forum looking to purchase logs
Once IABs have established a foothold in a company’s network, the access itself is then auctioned off on dark web forums.
Depending on the level of access provided, these auctions can be valuable to ransomware affiliates as an “easy” entry point for a ransomware attack.
How Stealer Logs Can Impact Consumers and Organizations
Stealer logs constitute a danger to consumer and organizations alike, with consumers (the victim of the infection) at risk of being victim of financial fraud or cryptocurrency theft, as well as unauthorized access to their accounts, but a surprising amount of stealer logs also provide some corporate access to various services.
A recent Flare analysis found more than 350,000 logs that contained credentials to commonly used corporate applications including single-sign on (SSO) portals, access to cloud environments, and other high-value applications.
Stealer Log Detection & Remediation with Flare
Flare automates detection for corporate credentials across tens of millions of stealer logs, providing contextualized high-value alerting to security teams.
Flare’s SaaS platform automatically detects the leading threats that lead to ransomware attacks, data breaches, and other forms of cybercrime affecting organizations.
Sign up for a free trial to find out how Flare can seamlessly integrate high-value cybercrime intelligence into your security program in 30 minutes.
Sponsored and written by Flare
Siemens Address Processing in SIMATIC
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.4
- ATTENTION: Exploitable remotely
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: SIMATIC, SIPLUS
- Vulnerability: Improper Input Validation
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to recover sensitive data or cause a denial-of-service condition.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
The following products from Siemens are affected:
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1504D TF (6ES7615-4DF10-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1504D TF (6ES7615-4DF10-0AB0): versions V3.0.1 to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1507D TF (6ES7615-7DF10-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1507D TF (6ES7615-7DF10-0AB0): versions V3.0.1 to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC ET 200SP Open Controller (incl. SIPLUS variants): all versions
- SIMATIC ET 200SP Open Controller CPU 1515SP PC2 (incl. SIPLUS variants): all versions
- SIMATIC IPC DiagBase: all versions
- SIMATIC IPC DiagMonitor: all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1200 CPU family (incl. SIPLUS variants): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6ES7510-1SJ00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6ES7510-1SJ01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6ES7510-1SK03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6ES7510-1DJ00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6ES7510-1DJ01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6ES7510-1DK03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AK00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AK02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AL03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511C-1 PN (6ES7511-1CK00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511C-1 PN (6ES7511-1CK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FK00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FK02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FL03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511T-1 PN (6ES7511-1TK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511T-1 PN (6ES7511-1TL03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511TF-1 PN (6ES7511-1UK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511TF-1 PN (6ES7511-1UL03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512C-1 PN (6ES7512-1CK00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512C-1 PN (6ES7512-1CK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6ES7512-1SK00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6ES7512-1SK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6ES7512-1SM03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6ES7512-1DK00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6ES7512-1DK01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6ES7512-1DM03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AL00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AL01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AL02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AM03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FL00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FL01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FL02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FM03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513R-1 PN (6ES7513-1RL00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513R-1 PN (6ES7513-1RM03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SP F-2 PN (6ES7514-2SN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SP-2 PN (6ES7514-2DN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SPT F-2 PN (6ES7514-2WN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SPT-2 PN (6ES7514-2VN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AM00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AM01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AM02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FM00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FM01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FM02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6ES7515-2RM00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6ES7515-2RN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515T-2 PN (6ES7515-2TM01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515T-2 PN (6ES7515-2TN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515TF-2 PN (6ES7515-2UM01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515TF-2 PN (6ES7515-2UN03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AN00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AN01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AN02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AP03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FN00-0AB0): all versions
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FN01-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FN02-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FP03-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516T-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3TN00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516TF-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3UN00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3AP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517F-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3FP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517H-3 PN (6ES7517-3HP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517T-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3TP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517TF-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3UP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4AP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP MFP (6ES7518-4AX00-1AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4FP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP MFP (6ES7518-4FX00-1AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518HF-4 PN (6ES7518-4JP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518T-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4TP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518TF-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4UP00-0AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU S7-1518-4 PN/DP ODK (6ES7518-4AP00-3AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU S7-1518F-4 PN/DP ODK (6ES7518-4FP00-3AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1513PRO F-2 PN (6ES7513-2GL00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1513PRO-2 PN (6ES7513-2PL00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1516PRO F-2 PN (6ES7516-2GN00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1516PRO-2 PN (6ES7516-2PN00-0AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIMATIC S7-1500 Software Controller: all versions
- SIMATIC S7-PLCSIM Advanced: all versions
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6AG1510-1SJ01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1SJ01-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6AG1510-1DJ01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6AG1510-1DJ01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1DJ01-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1DJ01-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6AG1512-1SK00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6AG1512-1SK01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6AG1512-1SK01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1SK01-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1SK01-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6AG1512-1DK01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6AG1512-1DK01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1DK01-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1DK01-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK02-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN T1 RAIL (6AG2511-1AK01-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN T1 RAIL (6AG2511-1AK02-1AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN TX RAIL (6AG2511-1AK01-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN TX RAIL (6AG2511-1AK02-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6AG1511-1FK00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6AG1511-1FK01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6AG1511-1FK02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL02-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6AG1513-1FL00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6AG1513-1FL01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6AG1513-1FL02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6AG1515-2FM01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6AG1515-2FM02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN RAIL (6AG2515-2FM02-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN T2 RAIL (6AG2515-2FM01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6AG1515-2RM00-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN TX RAIL (6AG2515-2RM00-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN00-7AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN01-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN02-7AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3AN02-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP TX RAIL (6AG2516-3AN01-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3FN00-2AB0): all versions
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3FN02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3FN01-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3FN02-2AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3FN02-4AB0): versions prior to V2.9.7
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1517H-3 PN (6AG1517-3HP00-4AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP (6AG1518-4AP00-4AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP MFP (6AG1518-4AX00-4AC0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP (6AG1518-4FP00-4AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518HF-4 PN (6AG1518-4JP00-4AB0): versions prior to V3.0.3
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 IMPROPER INPUT VALIDATION CWE-20
There is a type confusion vulnerability relating to X.400 address processing inside an X.509 GeneralName. This vulnerability may allow an attacker to pass arbitrary pointers to a memcmp call, enabling them to read memory contents or enact a denial of service.
CVE-2023-0286 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.4 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:H/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:N/A:H).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Siemens reported this vulnerability to CISA.
4. MITIGATIONS
Siemens has released updates for several affected products and recommends updating to the latest versions. Siemens is preparing further updates and recommends specific countermeasures for products where updates are not, or not yet available:
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1504D TF (6ES7615-4DF10-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1504D TF (6ES7615-4DF10-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1507D TF (6ES7615-7DF10-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC Drive Controller CPU 1507D TF (6ES7615-7DF10-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6ES7510-1SJ01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6ES7510-1SK03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6ES7510-1DJ01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6ES7510-1DK03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AK02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6ES7511-1AL03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511C-1 PN (6ES7511-1CK00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511C-1 PN (6ES7511-1CK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FK02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6ES7511-1FL03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511T-1 PN (6ES7511-1TK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511T-1 PN (6ES7511-1TL03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511TF-1 PN (6ES7511-1UK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1511TF-1 PN (6ES7511-1UL03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512C-1 PN (6ES7512-1CK00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512C-1 PN (6ES7512-1CK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6ES7512-1SK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6ES7512-1SM03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6ES7512-1DK01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6ES7512-1DM03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AL01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AL02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6ES7513-1AM03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FL01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FL02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6ES7513-1FM03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513R-1 PN (6ES7513-1RL00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1513R-1 PN (6ES7513-1RM03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SP F-2 PN (6ES7514-2SN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SP-2 PN (6ES7514-2DN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SPT F-2 PN (6ES7514-2WN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1514SPT-2 PN (6ES7514-2VN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AM01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AM02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515-2 PN (6ES7515-2AN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FM01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FM02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6ES7515-2FN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6ES7515-2RM00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6ES7515-2RN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515T-2 PN (6ES7515-2TM01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515T-2 PN (6ES7515-2TN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515TF-2 PN (6ES7515-2UM01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1515TF-2 PN (6ES7515-2UN03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AN01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AN02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3AP03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FN01-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FN02-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3FP03-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516T-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3TN00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1516TF-3 PN/DP (6ES7516-3UN00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3AP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517F-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3FP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517H-3 PN (6ES7517-3HP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517T-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3TP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1517TF-3 PN/DP (6ES7517-3UP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4AP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP MFP (6ES7518-4AX00-1AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4FP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP MFP (6ES7518-4FX00-1AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518HF-4 PN (6ES7518-4JP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518T-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4TP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU 1518TF-4 PN/DP (6ES7518-4UP00-0AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU S7-1518-4 PN/DP ODK (6ES7518-4AP00-3AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 CPU S7-1518F-4 PN/DP ODK (6ES7518-4FP00-3AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1513PRO F-2 PN (6ES7513-2GL00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1513PRO-2 PN (6ES7513-2PL00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1516PRO F-2 PN (6ES7516-2GN00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIMATIC S7-1500 ET 200pro: CPU 1516PRO-2 PN (6ES7516-2PN00-0AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP F-1 PN (6AG1510-1SJ01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1SJ01-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6AG1510-1DJ01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN (6AG1510-1DJ01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1DJ01-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1510SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2510-1DJ01-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6AG1512-1SK01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN (6AG1512-1SK01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1SK01-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP F-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1SK01-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6AG1512-1DK01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN (6AG1512-1DK01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1DK01-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS ET 200SP CPU 1512SP-1 PN RAIL (6AG2512-1DK01-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN (6AG1511-1AK02-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN T1 RAIL (6AG2511-1AK01-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN T1 RAIL (6AG2511-1AK02-1AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN TX RAIL (6AG2511-1AK01-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511-1 PN TX RAIL (6AG2511-1AK02-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6AG1511-1FK01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1511F-1 PN (6AG1511-1FK02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513-1 PN (6AG1513-1AL02-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6AG1513-1FL01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1513F-1 PN (6AG1513-1FL02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6AG1515-2FM01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN (6AG1515-2FM02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN RAIL (6AG2515-2FM02-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515F-2 PN T2 RAIL (6AG2515-2FM01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN (6AG1515-2RM00-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1515R-2 PN TX RAIL (6AG2515-2RM00-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN01-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3AN02-7AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3AN02-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516-3 PN/DP TX RAIL (6AG2516-3AN01-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3FN02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP (6AG1516-3FN01-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3FN02-2AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1516F-3 PN/DP RAIL (6AG2516-3FN02-4AB0): Update to V2.9.7 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1517H-3 PN (6AG1517-3HP00-4AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP (6AG1518-4AP00-4AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518-4 PN/DP MFP (6AG1518-4AX00-4AC0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518F-4 PN/DP (6AG1518-4FP00-4AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
- SIPLUS S7-1500 CPU 1518HF-4 PN (6AG1518-4JP00-4AB0): Update to V3.0.3 or later
Siemens has identified the following specific workarounds and mitigations users can apply to reduce risk:
- Disable CRL (certification revocation list) checking, if possible
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following recommendations in the product manuals. Additional information on industrial security by Siemens can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT
For more information see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-264815 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of this vulnerability. Specifically, users should:
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the Internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from business networks.
- When remote access is required, use secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
No known public exploitation specifically targeting this vulnerability has been reported to CISA at this time. This vulnerability has a high attack complexity.
Siemens RUGGEDCOM CROSSBOW
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 9.8
- ATTENTION: Exploitable remotely/low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: RUGGEDCOM CROSSBOW
- Vulnerabilities: Out-of-bounds Read, Improper Privilege Management, SQL Injection, Missing Authentication for Critical Function
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary database queries via SQL injection attacks, create a denial-of-service condition, or write arbitrary files to the application's file system.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
Siemens reports that the following server application is affected:
- RUGGEDCOM CROSSBOW: Versions prior to V5.4
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
An issue found in SQLite3 v.3.35.4 that could allow a remote attacker to cause a denial of service via the appendvfs.c function.
CVE-2021-31239 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.5 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:H).
3.2.2 IMPROPER PRIVILEGE MANAGEMENT CWE-269
Microsoft Windows Defender has an elevation of privilege vulnerability. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain specific limited SYSTEM privileges. This vulnerability could allow an attacker to delete data, which could include data that results in the service being unavailable.
CVE-2022-37971 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.1 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:H).
3.2.3 SQL INJECTION CWE-89
The affected application is vulnerable to SQL injection. This could allow an authenticated remote attacker to execute arbitrary SQL queries on the server database and escalate privileges.
CVE-2023-27411 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 8.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.4 SQL INJECTION CWE-89
The affected application is vulnerable to SQL injection. This could allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to execute arbitrary SQL queries on the server database.
CVE-2023-37372 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 9.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.5 MISSING AUTHENTICATION FOR CRITICAL FUNCTION CWE-306
The affected application accepts unauthenticated file write messages. An unauthenticated remote attacker could write arbitrary files to the affected application's file system.
CVE-2023-37373 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 5.3 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:H/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:N).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple Sectors
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) reported these vulnerabilities to Siemens.
4. MITIGATIONS
iemens has released an update for RUGGEDCOM CROSSBOW and recommends updating to the latest version:
- RUGGEDCOM CROSSBOW: Update to V5.4 or later versions.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to the Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following product manual recommendations.
Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage.
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information, see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-472630 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Specifically, users should:
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the Internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from business networks.
- When remote access is required, use secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
CISA also recommends users take the following measures to protect themselves from social engineering attacks:
- Do not click web links or open attachments in unsolicited email messages.
- Refer to Recognizing and Avoiding Email Scams for more information on avoiding email scams.
- Refer to Avoiding Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks for more information on social engineering attacks.
No known public exploitation specifically targeting these vulnerabilities has been reported to CISA at this time. These vulnerabilities are exploitable remotely. These vulnerabilities have low attack complexity.
Siemens JT Open, JT Utilities, and Parasolid
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.8
- ATTENTION: Low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: JT Open, JT Utilities, and Parasolid
- Vulnerabilities: Out-of-bounds Read
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
The following products from Siemens are affected:
- JT Open: All versions prior to v11.4
- JT Utilities: All versions prior to v13.4
- Parasolid v34.0: All versions prior to v34.0.253
- Parasolid v34.1: All versions prior to v34.1.243
- Parasolid v35.0: All versions prior to v35.0.177
- Parasolid v35.1: All versions prior to v35.1.073
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted JT files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-30795 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.2 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted JT files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-30796 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple Sectors
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Michael Heinzl reported these vulnerabilities to Siemens.
4. MITIGATIONS
Siemens released updates for the affected products and recommends updating to the latest versions:
- Parasolid V35.1: Update to V35.1.073 or later version.
- Parasolid V35.0: Update to V35.0.177 or later version.
- Parasolid V34.1: Update to V34.1.243 or later version.
- Parasolid V34.0: Update to V34.0.253 or later version.
- JT Utilities: Update to V13.4 or later version.
- JT Open: Update to V11.4 or later version.
Siemens identified the following specific workarounds and users can apply to reduce risk:
- Do not open untrusted files using Parasolid, JT Open Toolkit, or JT Utilities.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to the Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following recommendations in the product manuals.
Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information, see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-001569 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Specifically, users should:
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the Internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from business networks.
- When remote access is required, use secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
No known public exploits specifically target these vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities are not exploitable remotely.
Siemens Parasolid and Teamcenter Visualization
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.8
- ATTENTION: Low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: Parasolid and Teamcenter Visualization
- Vulnerabilities: NULL Pointer Dereference, Out-of-bounds Read, Out-of-bounds Write, Allocation of Resources without Limits or Throttling
2. RISK EVALUATION
An attacker could successfully exploit these vulnerabilities by tricking a user into opening a malicious file, allowing the attacker to cause a denial of service or perform remote code execution in the context of the current process.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
Siemens reports that the following products are affected:
- Parasolid V34.1: versions prior to V34.1.258
- Parasolid V35.0: versions prior to V35.0.254
- Parasolid V35.1: versions prior to V35.1.171
- Parasolid V35.1: versions prior to V35.1.197
- Parasolid V35.1: versions prior to V35.1.184
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.1: all versions
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.2: versions prior to V14.2.0.6
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.3: all versions
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 NULL POINTER DEREFERENCE CWE-476
The affected applications contain null pointer dereference while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38524 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 3.3 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:L).
3.2.2 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38525 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.3 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38526 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.4 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38527 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.5 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38529 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.6 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38530 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.7 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted X_T files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38531 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.8 OUT-OF-BOUNDS WRITE CWE-787
The affected application contains an out-of-bounds write past the end of an allocated buffer while parsing a specially crafted X_T file. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38528 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.9 ALLOCATION OF RESOURCES WITHOUT LIMITS OR THROTTLING CWE-770
The affected application contains a stack exhaustion vulnerability while parsing a specially crafted X_T file. This could allow an attacker to cause denial of service condition.
CVE-2023-38532 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 6.6 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:L/I:L/A:H).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Critical Manufacturing
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Siemens reported these vulnerabilities to CISA.
4. MITIGATIONS
Siemens released updates for several affected products and recommends updating to the latest versions. Siemens is preparing further updates for Teamcenter Visualization V14.1 and V14.3; fixes are planned for the next patch release:
- Parasolid V34.1: Update to V34.1.258 or later version.
- Parasolid V35.0: Update to V35.0.254 or later version.
- Parasolid V35.1: Update to V35.1.171 or later version.
- Parasolid V35.1: Update to V35.1.197 or later version.
- Parasolid V35.1: Update to V35.1.184 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.2: Update to V14.2.0.6 or later version.
Siemens identified the following specific workaround/mitigation users can apply to reduce risk:
- Do not open untrusted X_T files in Parasolid or Teamcenter Visualization.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to the Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following recommendations in the product manuals. Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage.
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information, see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-407785 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of these vulnerabilities. CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
CISA also recommends users take the following measures to protect themselves from social engineering attacks:
- Do not click web links or open attachments in unsolicited email messages.
- Refer to Recognizing and Avoiding Email Scams for more information on avoiding email scams.
- Refer to Avoiding Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks for more information on social engineering attacks.
No known public exploitation specifically targeting these vulnerabilities has been reported to CISA at this time. These vulnerabilities are not exploitable remotely. These vulnerabilities have low attack complexity.
Siemens Solid Edge, JT2Go, and Teamcenter Visualization
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.8
- ATTENTION: Low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: Solid Edge, JT2Go, and Teamcenter Visualization
- Vulnerabilities: Use After Free, Out-of-bounds Read, Out-of-bounds Write
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
The following products from Siemens are affected:
- JT2Go: All versions prior to v14.2.0.5
- Solid Edge SE2022: All versions prior to v222.0 Update 13
- Solid Edge SE2023: All versions prior to v223.0 Update 4
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.2: All versions prior to v13.2.0.15
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.2: All versions prior to v13.2.0.14
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.3: All versions prior to v13.3.0.11
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.1: All versions prior to v14.1.0.11
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.1: All versions prior to v14.1.0.10
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.2: All versions prior to v14.2.0.5
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 USE AFTER FREE CWE-416
The affected application contains a use-after-free vulnerability that could be triggered while parsing specially crafted ASM file. An attacker could leverage this vulnerability to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-28830 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.2 OUT-OF-BOUNDS READ CWE-125
The affected applications contain an out-of-bounds read past the end of an allocated structure while parsing specially crafted TIFF files. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38682 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.3 OUT-OF-BOUNDS WRITE CWE-787
The affected application contains an out-of-bounds write past the end of an allocated buffer while parsing a specially crafted TIFF file. This could allow an attacker to execute code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2023-38683 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple Sectors
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Jin Huang from ADLab of Venustech and Michael Heinzl reported these vulnerabilities to Siemens.
4. MITIGATIONS
iemens released updates for the affected products and recommends updating to the latest versions:
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.1: Update to V14.1.0.10 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.2: Update to V13.2.0.14 or later version.
- Solid Edge SE2023: Update to V223.0 Update 4 or later version.
- Solid Edge SE2022: Update to V222.0 Update 13 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.2: Update to V14.2.0.5 or later version.
- JT2Go: Update to V14.2.0.5 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V14.1: Update to V14.1.0.11 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.3: Update to V13.3.0.11 or later version.
- Teamcenter Visualization V13.2: Update to V13.2.0.15 or later version.
Siemens identified the following specific workarounds and mitigations users can apply to reduce risk:
- Avoid opening untrusted files in JT2Go, Teamcenter Visualization, and Solid Edge.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following product manual recommendations.
Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage.
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information, see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-131450 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of these vulnerabilities. CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
CISA also recommends users take the following measures to protect themselves from social engineering attacks:
- Do not click web links or open attachments in unsolicited email messages.
- Refer to Recognizing and Avoiding Email Scams for more information on avoiding email scams.
- Refer to Avoiding Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks for more information on social engineering attacks.
No known public exploits specifically target this these vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities are not exploitable remotely.
Siemens Parasolid Installer
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.8
- ATTENTION: Low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: Parasolid
- Vulnerability: Incorrect Permission Assignment for Critical Resource
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to misuse the vulnerability and escalate privileges.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
The following products from Siemens are affected if installed with Parasolid installer:
- Parasolid V35.0: All versions
- Parasolid V35.1: All versions
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 INCORRECT PERMISSION ASSIGNMENT FOR CRITICAL RESOURCE CWE-732
Nullsoft Scriptable Install System (NSIS) before v3.09 creates an "uninstall directory" with insufficient access control. This could allow an attacker to misuse the vulnerability and escalate privileges.
CVE-2023-37378 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple Sectors
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Siemens reported this vulnerability to CISA.
4. MITIGATIONS
nly systems on which Parasolid is installed with a Parasolid installer is impacted. Siemens recommends uninstalling impacted Parasolid instances and reinstalling with the latest available installer:
- Parasolid v35.0: Latest installer.
- Parasolid v35.1: Latest installer.
Siemens identified the following specific workarounds and mitigations users can apply to reduce risk:
- Scan each computer on which Parasolid has ever been installed with an up-to-date anti-virus program and follow its recommendations.
- Ensure only trusted persons have access to the system and avoid the configuration of additional accounts.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following product manual recommendations.
Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage.
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-116172 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of this vulnerability. Specifically, users should:
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the Internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from business networks.
- When remote access is required, use secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
No known public exploits specifically target this vulnerability. This vulnerability is not exploitable remotely.
Siemens Software Center
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- CVSS v3 7.8
- ATTENTION: Exploitable remotely/low attack complexity
- Vendor: Siemens
- Equipment: Software Center
- Vulnerabilities: Uncontrolled Search Path Element, Path Traversal
2. RISK EVALUATION
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow a local attacker to execute code with elevated privileges.
3. TECHNICAL DETAILS
3.1 AFFECTED PRODUCTS
The following products from Siemens are affected:
- Siemens Software Center: All versions prior to v3.0
3.2 VULNERABILITY OVERVIEW
3.2.1 UNCONTROLLED SEARCH PATH ELEMENT CWE-427
A DLL hijacking vulnerability could allow a local attacker to execute code with elevated privileges by placing a malicious DLL in one of the directories on the DLL search path.
CVE-2021-41544 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.8 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
3.2.2 IMPROPER LIMITATION OF A PATHNAME TO A RESTRICTED DIRECTORY ('PATH TRAVERSAL') CWE-22
Qt through 5.15.8 and 6.x through 6.2.3 could load system library files from an unintended working directory.
CVE-2022-25634 has been assigned to this vulnerability. A CVSS v3 base score of 7.5 has been calculated; the CVSS vector string is (AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:N/A:N).
3.3 BACKGROUND
- CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE SECTORS: Multiple Sectors
- COUNTRIES/AREAS DEPLOYED: Worldwide
- COMPANY HEADQUARTERS LOCATION: Germany
3.4 RESEARCHER
Samuel Hanson from Dragos reported these vulnerabilities to Siemens.
4. MITIGATIONS
Siemens released an update V3.0 for the Siemens Software Center and recommends users update to the latest version. Existing installations of SSC will be prompted to update whenever a new version is available.
Siemens identified the following specific workarounds and mitigations users can apply to reduce risk:
- Harden the application host to prevent local access by untrusted personnel.
As a general security measure, Siemens recommends protecting network access to devices with appropriate mechanisms. To operate the devices in a protected IT environment, Siemens recommends configuring the environment according to Siemens' operational guidelines for industrial security and following recommendations in the product manuals.
Additional information on Siemens industrial security can be found on the Siemens industrial security webpage.
For further inquiries on security vulnerabilities in Siemens products and solutions, please contact the Siemens ProductCERT.
For more information, see the associated Siemens security advisory SSA-188491 in HTML and CSAF.
CISA recommends users take defensive measures to minimize the risk of exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Specifically, users should:
- Minimize network exposure for all control system devices and/or systems, and ensure they are not accessible from the Internet.
- Locate control system networks and remote devices behind firewalls and isolate them from business networks.
- When remote access is required, use secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), recognizing VPNs may have vulnerabilities and should be updated to the most current version available. Also recognize VPN is only as secure as its connected devices.
CISA reminds organizations to perform proper impact analysis and risk assessment prior to deploying defensive measures.
CISA also provides a section for control systems security recommended practices on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics. Several CISA products detailing cyber defense best practices are available for reading and download, including Improving Industrial Control Systems Cybersecurity with Defense-in-Depth Strategies.
Additional mitigation guidance and recommended practices are publicly available on the ICS webpage at cisa.gov/ics in the technical information paper, ICS-TIP-12-146-01B--Targeted Cyber Intrusion Detection and Mitigation Strategies.
Organizations observing suspected malicious activity should follow established internal procedures and report findings to CISA for tracking and correlation against other incidents.
CISA also recommends users take the following measures to protect themselves from social engineering attacks:
- Do not click web links or open attachments in unsolicited email messages.
- Refer to Recognizing and Avoiding Email Scams for more information on avoiding email scams.
- Refer to Avoiding Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks for more information on social engineering attacks.
No known public exploits specifically target these vulnerabilities.
New Attack Alert: Freeze[.]rs Injector Weaponized for XWorm Malware Attacks
Malicious actors are using a legitimate Rust-based injector called Freeze[.]rs to deploy a commodity malware called XWorm in victim environments. The novel attack chain, detected by Fortinet FortiGuard Labs on July 13, 2023, is initiated via a phishing email containing a booby-trapped PDF file. It has also been used to introduce Remcos RAT by means of a crypter called SYK Crypter, which was
Identity management platform Veza secures $15M from Capital One and ServiceNow
Veza, a platform that helps to secure identity access across apps, data systems and cloud infrastructure, today announced that it raised $15 million in a funding round led by Capital One Ventures and ServiceNow — valuing the company at $415 million. Bringing Veza’s total raised to $125 million, co-founder and CEO Tarun Thakur says that […]