this post was submitted on 10 Aug 2024
689 points (98.2% liked)
Science Memes
11047 readers
3574 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
This is a science community. We use the Dawkins definition of meme.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
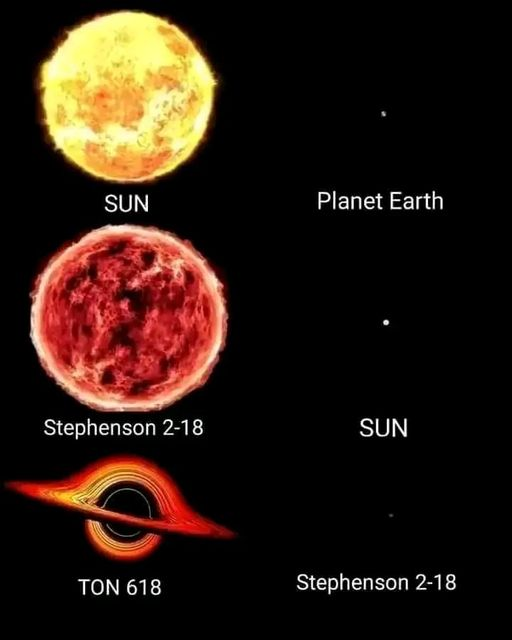
Astrophysicist here. Yes, space is crazy, but interesting things to keep in mind:
Hi Astrophysics,
I always wondered why they draw black holes like they do in that the accretion looks like it's drawn in two planes. I would have thought it would have looked a bit more like a saturns rings? Or is it exactly like saturns rings but we see the whole ring bent round the top because a black hole bends the light around so we can see it? Or is it something else entirely that they are trying to depict here?
Yep, you got it right. The accretion disk is actually really flat. Those images are produced in simulations that take into account the curved (and very complex) paths light takes in the vicinity of a black hole. These images really depend on the angle between the line of sight and the disk.