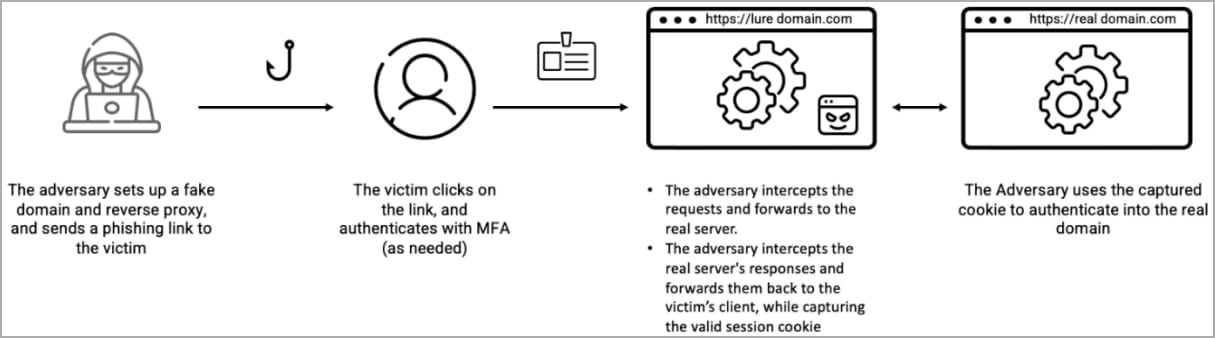
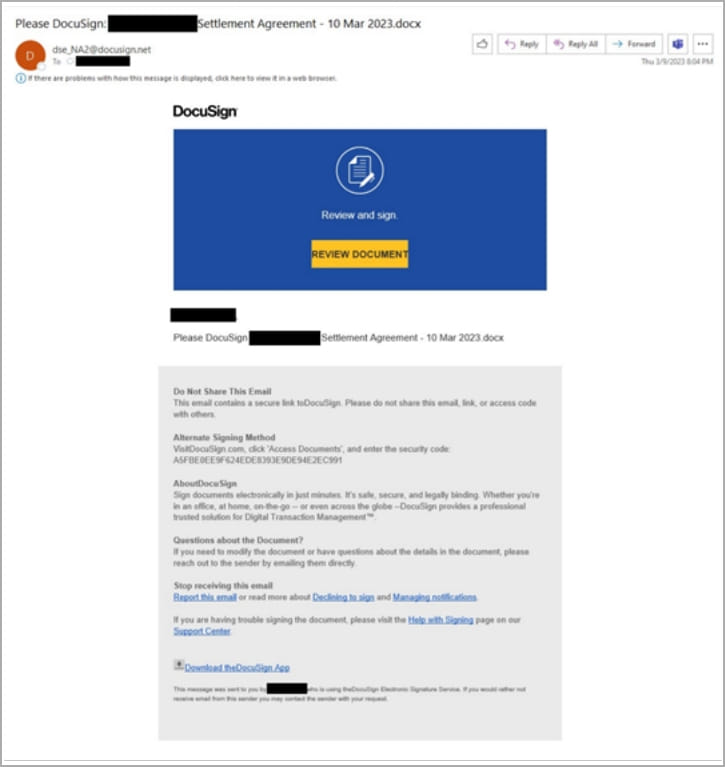
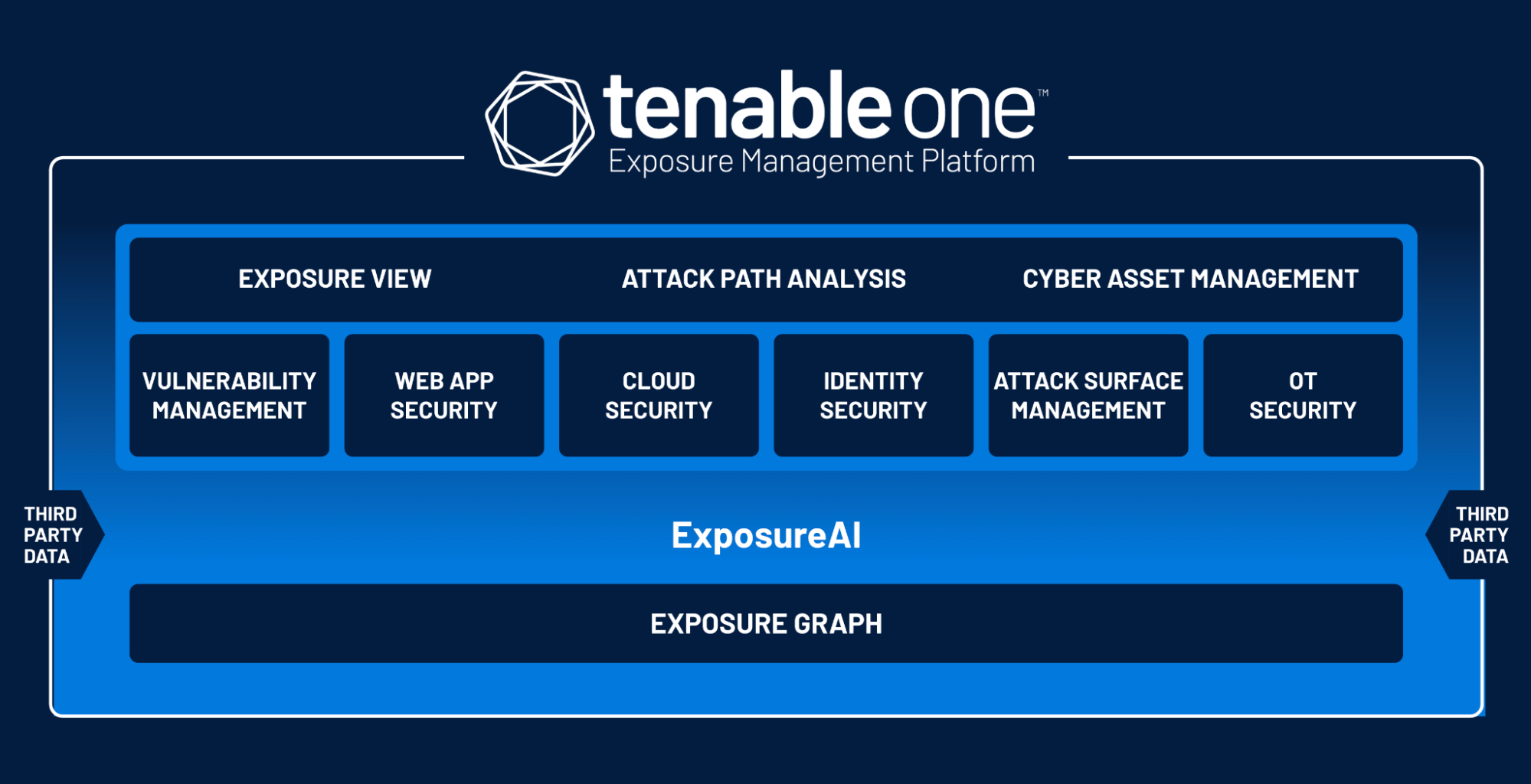
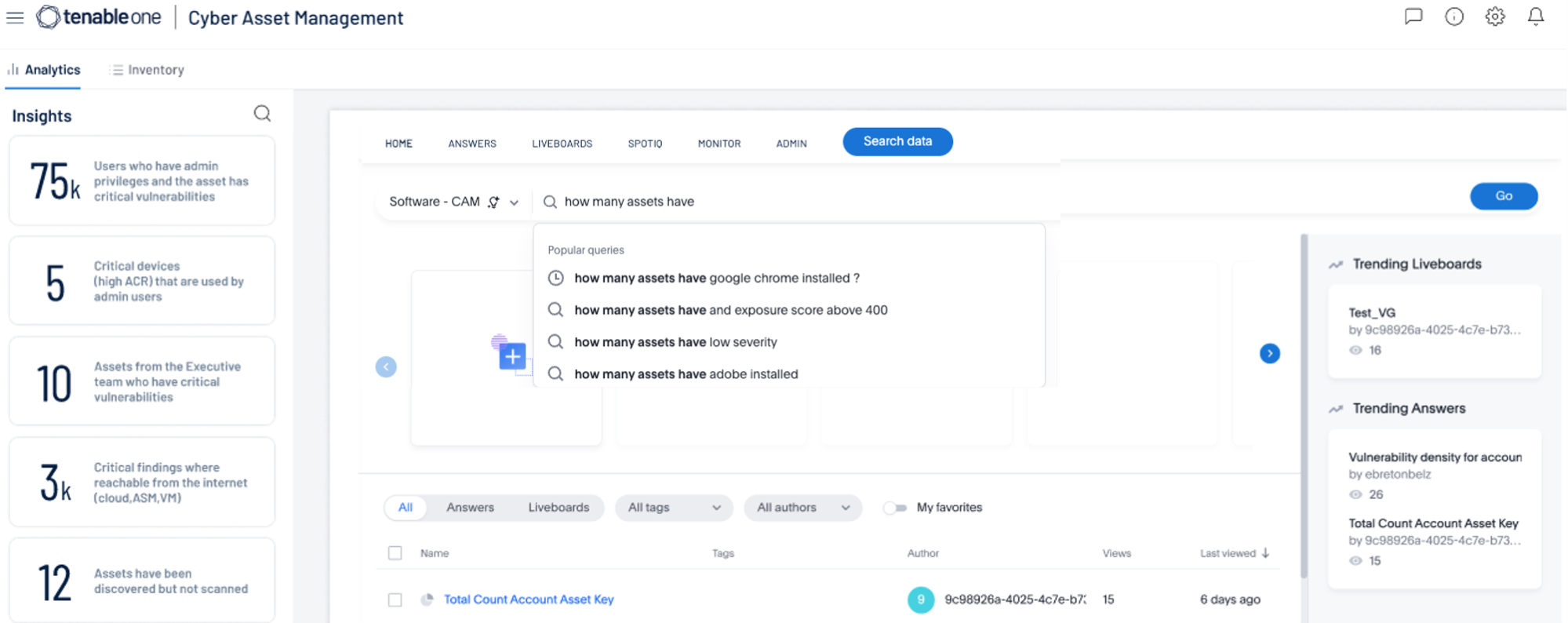
The widespread adoption of a digital transformation workspace and the shift to web applications has led to a global rise in cybercrime, with 2022 seeing an 87% year-over-year increase in IoT malware attacks.
With vast storehouses of sensitive data, newly adopted Internet of Medical Things technology, and often outdated cybersecurity systems, the healthcare industry has become a prime target for industrious cyber criminals seeking to exploit industry vulnerabilities for profit. Cyberattacks are on the rise in these industries and the attempted cyberattacks that target online apps rose by a notable 137% during the last year.
In this article, we will take a look at why healthcare organizations are at increased risk for cyberattacks. We will explore what the Internet of Medical Things is and will investigate how healthcare organizations should best assess the security of their networks.
We will then reveal why and how HIPAA plays a role in securing sensitive medical data and how attack surface management can secure the IoMT for healthcare organizations.
Why healthcare organizations are at increased risk for cyberattacks
Due to outdated technical systems and wide-ranging points of entry, there is a large potential for entry for savvy threat actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in the healthcare industry.
Since healthcare industry organizations are frequently running apps with inadequate protection and insufficient security precautions, the healthcare sector is a particular target for app-based and API-based attacks.
Healthcare organizations will need to embrace web application security testing to secure applications and stay on top of vulnerabilities from the latest cyberattack schemes.
Using broken object-level authorization (or BOLA) methods, hackers can adjust the identification of a particular object in the context of an API command.
This access allows hackers to manipulate the identity of the request, providing an easy access point for users to completely bypass gatekeeping measures and read restricted data. Unauthorized users can even erase a user’s private data.
This type of attack offers a wide range of potential for manipulating and extorting healthcare organizations, whose databases contain an abundant of sensitive information about patient medical histories, current health records, home addresses, and financial details.
What is the internet of medical things?
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to the interconnected network of communication technologies that transmits data in real-time through a cloud computing structure, which can be used for Smart Health applications.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is an offshoot of the widely popular Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT provides enhanced AI-enabled communication between a wide variety of devices, including mobile phones, wearable devices, industrial sensors, and actuating ports, which convey information through cloud storage databases.
The IoT is used to connect smart homes, power smart cars, sync smart cities, establish smart energy grids, and enhance smart retail, among other uses.
The Internet of Medical Things, meanwhile, provides data communication among mobile computers, medical sensors, and cloud computation software. The syncing of these devices allows medical experts to monitor and conduct analyses of a patient’s vital signs and health progress.
Medical professionals can utilize the advanced capabilities provided by the IoMT to assess, diagnose, treat, and track patient conditions.
Given the amount of sensitive data that is transmitted via smart health devices, it is vital for healthcare organizations to secure the Internet of Medical Things. The data that is communicated through devices that combine to form the IoMT is transmitted through layered cloud computing platforms that medical professionals can access via web-based applications that draw data from the cloud.
These cloud data storage platforms can include database storage, access portals for various clients and professionals, and the exchange of Electronic Medical Records, or EMRs. Some interconnected IoMT devices can also offer patient portals so that patients can access their medical records and up-to-date information on their conditions in real-time.
How to assess the security of your healthcare organization?
Conducting an effective risk assessment process will allow IT experts and security managers to assess the overall cybersecurity level of your healthcare organization.
From basic individual security measures, such as a general secure password policy, to specific security patches that will need to be enacted, a security risk assessment should cover the entire breadth of your healthcare organization’s security approach.
A security risk assessment will identify any potential weak spots and vulnerable assets in the healthcare organization’s digital infrastructure, including specific employee training and awareness.
This risk assessment should include assembling an inventory of all of your organization’s assets to understand what is at risk of being compromised in the event of a successful cyberattack.
With this inventory in hand, you will be able to calculate the likely damages that could result to your healthcare organization in the event of a successful cyberattack.
For example, if a bad actor is able to access your organization’s EHR (electronic health records), your organization may find it necessary to halt all patient treatments and procedures until the records are reclaimed and secured. Or, your organization could incur fines for failing to comply with nationwide regulatory measures.
Your risk assessment process should include a comprehensive analysis of every possible threat, vulnerable situation, and exposed data. Natural disasters such as floods or blackouts can lead to exposed vulnerable databases, while insidious interpersonal attacks can come in the form of phishing emails, or DDoS, distributed denial-of-service attacks on the healthcare organization servers.
Embittered former employees with access to restricted servers and databases could enact their dissatisfaction via malicious tampering with sensitive data. Any risk situations should be considered to accurately assess the organization’s overall security situation- and will allow the right individuals to prevent and mitigate lasting damages.
How/why does HIPAA play a role?
HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, provides nationwide regulations that ensure that each healthcare organization complies with the latest baseline security measures. HIPAA provides guidelines that can instruct healthcare organizations on how to craft effective contingency plans that help mitigate the damages in unexpected situations, such as a fire or flood.
For instance, to comply with HIPAA regulations, healthcare organizations must maintain three copies of their entire database at a minimum. These three copies must be stored in at least two distinct types of media, and one of these three copies of data must be stored offsite. If an organization fails to meet the basic requirements mandated by HIPAA, they may be subject to ample fines as a consequence.
The United States Department of Health and Human Services, or HHS, released the HIPAA Privacy Rule to guarantee that healthcare organizations will remain in compliance with HIPAA standards.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule protects sensitive data that contains a patient’s health information from being released or shared without the explicit consent and knowledge of the patient in question. This rule encompasses both the sharing of patient records among medical professionals and the protection of patient records against bad actors and cyberattacks.
How can attack surface management secure your IoT?
Attack surface management can be used to secure the IoMT for healthcare organizations by embracing a risk-based vulnerability management program. Reducing the areas of security vulnerabilities for bad actors reduces the possibility of enacting successful cyberattacks from the onset.
Most successful attacks are enacted through the penetration of vulnerable devices, which provide a surface for the attack.
Cloud-based databases, network services, firmware, specific individual devices, storage systems, servers, and web-based apps can each contribute to either the safety or vulnerability of an overall system’s robust security program.
Proactively managing, measuring, and reducing an organization's Internet-facing attack surface can significantly reduce the risk of a network breach.
Using a combination of specialist in-house expertise along with our proprietary automation platform and attack surface analysis tools, we can provide everything from a single point-in-time risk analysis to longer-term planning, execution, and metrics collection as you work to reduce your exposure to Internet-based attacks.
Attack surface management requires strong authentication safeguards to ensure that each user requesting access to a restricted area is amply verified before being admitted to accessing the data in question.
Automated exploitative tools will be prevented from gaining initial access to a restricted system, and weak authentication areas will be patched to create a more effective security foundation.
Attack surface management reduces an organization’s potential vulnerability to internet-based cyberattacks, which will directly impact the overall security of the interconnected IoMT devices and systems since all of the sensitive medical data is stored and communicating over the internet.
Final Thoughts
The healthcare industry is in a state of transition, with more organizations increasingly coming to rely on interconnected Smart Health devices that run off the IoMT.
The Internet of Medical Things provides an innovative way for updating medical practices and providing enhanced patient condition analysis and treatment procedures. But without adequate security measures, healthcare organizations will be open to increased security vulnerabilities.
Identifying all possible threats and vulnerabilities is key to establishing sufficient security measures that will provide comprehensive protection across all aspects of the healthcare organization’s digital network and in-house software systems.
Maintaining compliance with HIPAA guidelines and standards can assure that healthcare organizations have sufficient security measures in place.
Enacting attack surface management can help secure the internet on which Internet of Medical Things devices run. Protecting patient data and Electronic Medical Records is key for ensuring a secure medical system as IoMT technology continues to evolve.
Sponsored and written by Outpost24