Hackers claim to have breached the network of a major auction house and offered access to whoever was willing to pay $120,000.
Security researchers found the advertisement on a hacker forum known for providing a market for initial access brokers (IABs) after analyzing a sample of 72 posts.
Expensive network access
Researchers at threat intelligence company Flare poured through three months of IAB offers on the Russian-language hacker forum Exploit to better understand who they target, their ask prices, and who are the most active.
From May 1st until July 27, brokers advertised access to more than 100 companies across 18 industries including defense, telecommunications, healthcare, and financial services.
Eric Clay, vice president of marketing at Flare, says in a report shared with BleepingComputer that attacks against companies in the U.S., Australia, and the U.K. companies were the most common - not surprising given their high gross domestic product (GDP).
Organizations in the finance and retail sectors were the most targeted, followed by construction and manufacturing, Clay notes in the report.
Depending on the company profile and country, prices started at $150 and most of them were for initial access through VPN or RDP. About a third of the listings were under $1,000.
However, the most expensive item for sale was $120,000 (BTC 4 at the time) for access to the network of a multi-billion dollar auction house.
The hackers did not provide too many details but said they had privileged backend access to multiple high-end auctions (i.e. admin panel), like Stradivarius violins or collectible cars.
“While most access is low to medium value, occasionally extremely unique or high-value access is auctioned that can cause extreme pricing variation compared to our average” - Flare
Many other expensive offers were for initial access to companies in the U.S., and the U.K., initial access offers were for critical infrastructure organizations like healthcare, financial service, and manufacturing.
Access privilege and geography
Most of the posts mentioned the geograpy of the victim and researchers were able to create a map showing 35 allegedly hacked entities outside the U.S.
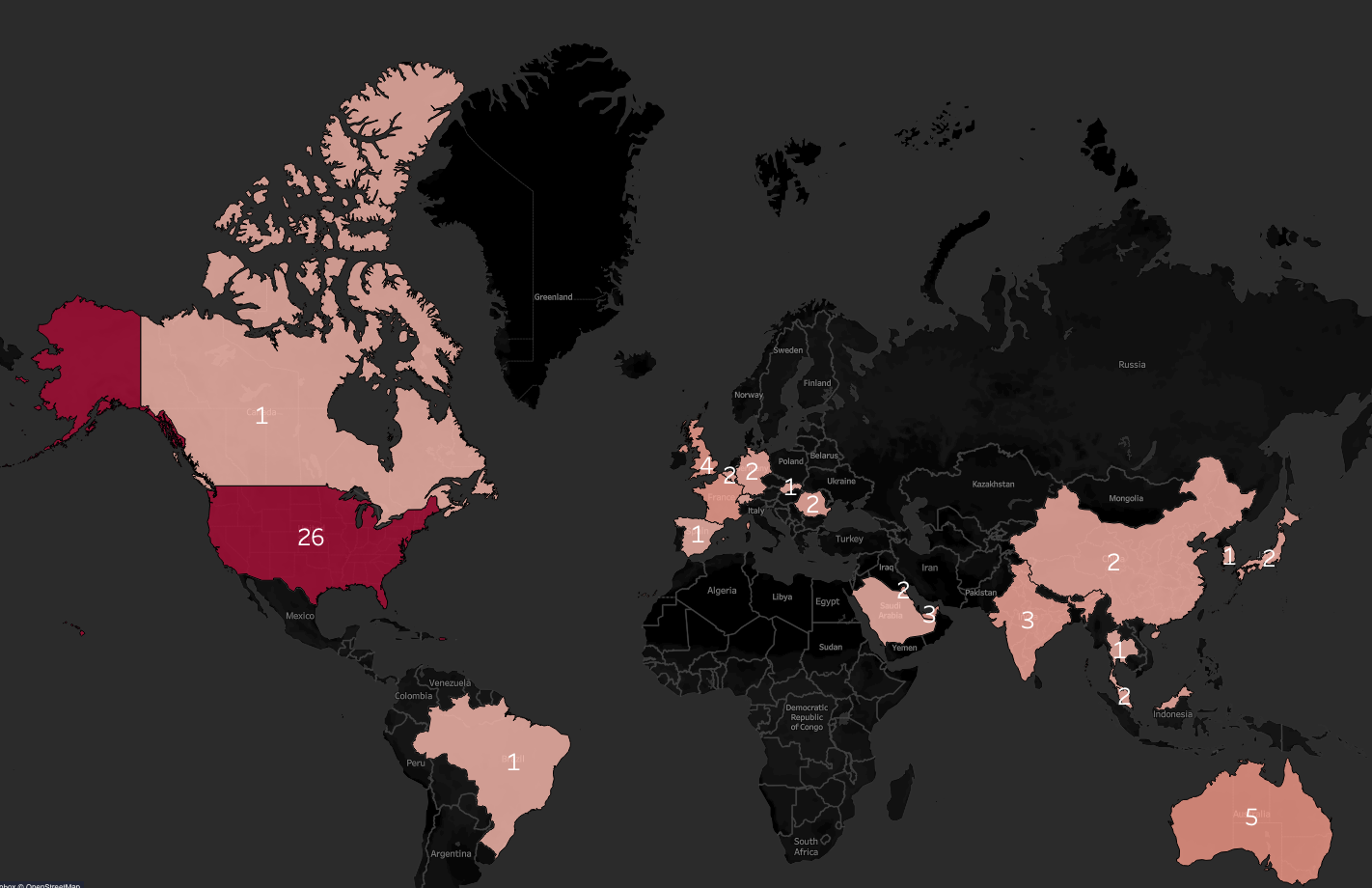
Victim distribution based on initial access advertisements
source: Flare.io
IABs on Exploit forum still avoid targets in Russia and countries in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) but a surprise is the small number in China, which has the second-highest GDP in the world.
Clay told BleepingComputer that while IABs typically avoid targeting China, there was one listing for network access to a Chinese artificial intelligence company.
The most frequent type of access seen in the posts was through RDP (seen in 32 posts) or VPN (seen in 11 posts), which together accounted for 60% of the listings in the data set.
The level of privileges associated with the access accounts ranged from cloud administrator (14 cases) to local admin (5 cases) and domain user (2 cases).
As a side note, Clay told BleepingComputer that one broker offered “privileged access to a U.S. radio station,” which hackers said could be used to “run ads.”
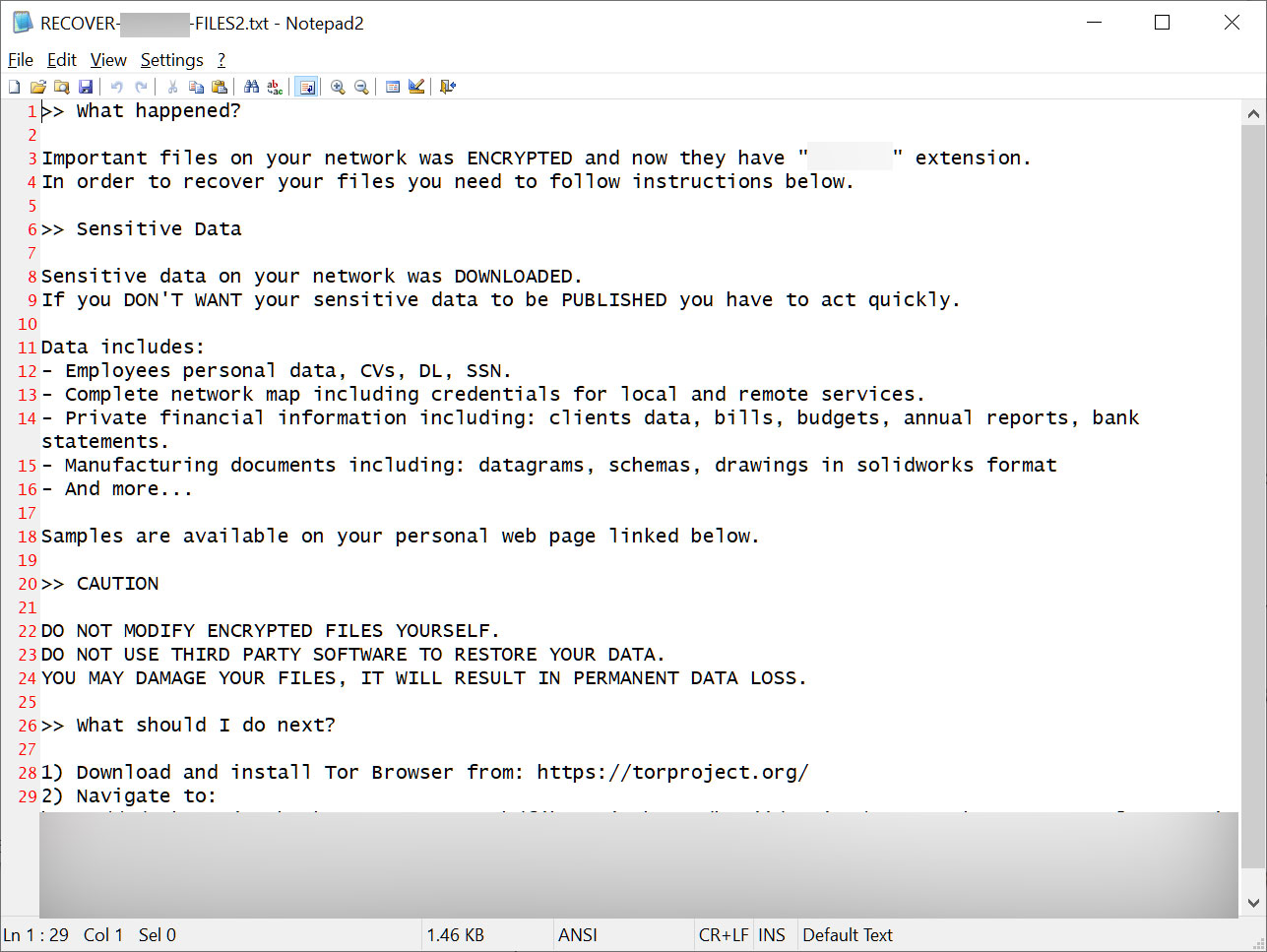
Some IABs advertised access to backup and recovery systems along with access to the corporate IT network, which could serve ransomware operations.
Typically, access to corporate networks comes from info-stealing malware but some actors clearly stated that they used a different method, likely some other type of malware, phishing, or exploiting a vulnerability.
“Stealer logs are an overlooked primary vector of access for initial access brokers, it's a surprisingly simple type of infection that is almost certain to be one of the major ways that IABs and ransomware groups are getting access to corporate IT environments" - Mathieu Lavoie. Chief Technology Officer at Flare
Regardless of the method initial access brokers used to obtain access to a network, companies should at least implement monitoring mechanisms for info-stealing malware, a regular source of corporate credentials.
Monitoring forums where initial access brokers advertise their offers may also help organizations get a clue about possible compromise even if the name of the victim is anonymized.
Combining data like geography, revenue, industry, and the type of access are enough hints to start an investigation into a potential breach.
This process can also come with positive side effects, such as uncovering areas that need stronger security or identifying devices, services, and accounts that could pose a risk.





.jpg)